The sun is about to undergo a significant departure: magnetic field reversal.
This phenomenon occurs approximately every 11 years and marks an important stage in the solar cycle. The shift in polarity marks the halfway point solar maximumthe height of solar activity, and the beginning of the transition towards solar minimum.
The last time the sunThe magnetic field was reversed towards the end of 2013. But what causes this change in polarity, and is it dangerous? We take an in-depth look at the reversal of the sun’s magnetic field and explore its potential effects World.
Related: How a giant sunspot unleashed solar storms that spawned global auroras that dazzled us all
To understand the reversal of the magnetic field, first, it is important to know the cycle of the sun. The approximately 11-year cycle of solar activity is driven by the sun’s magnetic field and is reflected in the sun’s frequency and intensity. sun spots visible on the surface. The height of solar activity during a given solar cycle is called the solar maximum, and current estimates predict that it will occur between late 2024 and early 2026.
But there is another very important, though lesser known, cycle that includes two 11-year solar cycles. Known as the Hale cycle, this magnetic cycle lasts about 22 years, during which the sun’s magnetic field reverses and then returns to its original state, Ryan Frenchsolar astrophysicist and Space.com contributing writer, said Space.com.
During solar minimum, the sun’s magnetic field is close to dipole, with one north pole and one south pole, like The Earth’s magnetic field. But as we move toward solar maximum, “the solar magnetic field becomes more complex, without a clear north-south pole separation,” French said. By the time solar maximum and solar minimum are reached, the sun has returned to dipole, although it had reversed polarity.
The upcoming change in polarity will be from the magnetic field north to south in the Northern Hemisphere and vice versa in the Southern Hemisphere. “This will bring it to a magnetic orientation similar to Earth, whose magnetic field is oriented south in the Northern Hemisphere,” French explained.
What causes the switch in polarity?
The reversal is driven by sunspots, magnetically complex regions of the sun’s surface that can spawn significant solar events, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) — large bursts of plasma and magnetic field.
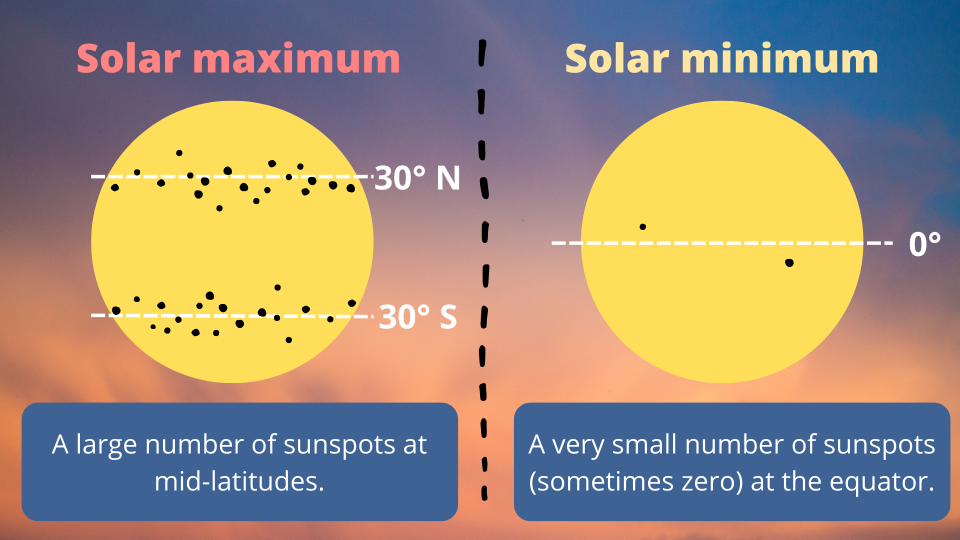
As sunspots develop near the equator, they will have an orientation that matches the old magnetic field, and sunspots closer to the poles will have a magnetic field that matches the incoming magnetic orientation. in, said the French. This is called Hale’s law.
“The magnetic field from active regions makes its way toward the poles and eventually causes the reversal,” solar physicist Todd Hoeksema, director of the Wilcox Solar Observatory at Stanford University, Space.com previously said.
But the root cause of such a flip in polarity remains mysterious. “That affects the whole thing [solar] cycle, and wondering what that is,” Stanford University solar physicist Phil Scherrer previously told Space.com. And until you can model it, you don’t really understand it — it’s really hard to understand .”
It really depends on where the magnetic field comes from. “Will there be a lot of sunspots? And will the sunspots add to the pole’s magnetic field, or cancel them out locally?” Hoeksema said. “That question we still do not know how to answer.”
How quickly does the switch occur?
Related stories:
—The solar flare causes the strongest radiation storm since 2017
—Mars’ solar storm douses in radiation and auroras flicker in the Red Planet’s sky (video)
—The astrophotographer captures stunning views near the sunspot region that spawns May’s auroras
What we do know is that the flip of the solar magnetic field is not instantaneous. It is a gradual transition from a dipole to a complex magnetic field, to a reverse dipole over the entire 11 year solar cycle. “In short, there is no particular ‘moment’ in which the solar poles flip,” French said. “It is not like the Earth, where the flip is measured by the migration of the North/South pole.”
It usually takes a year or two for a complete reversal, but it can vary greatly. For example, the northern polar region of Solar Cycle 24, which ended in December 2019, took nearly five years to reverse, according to the National Solar Observatory.
The magnetic field flip is so consistent, you won’t even notice when it happens. And no, as dramatic as it may sound, it is not a sign of an impending apocalypse. “The world will not end tomorrow,” Scherrer has been said before space.com.
However, we will experience some of the side effects of flipping polarity.
How does the sun’s magnetic flip affect us?


There is no doubt that the sun has been extremely active recently, firing off many powerful solar flares and CMEs, triggering strong geomagnetic storms on Earth, which, in turn, have produced several. Incredible auroral displays late.
However, on increased intensity space weather which is not the direct cause of the flip in polarity. Rather, these things tend to happen together, Hoeksema told Space.com in 2013.
Space weather is usually the strongest during solar maximum, when the sun’s magnetic field is also the most complex, according to France.
Shifting the magnetic field has one small but mostly beneficial side effect: It can help protect Earth from the galaxy cosmic rays — high-energy subatomic particles that travel at near-light speeds and can damage spacecraft and harm orbiting astronauts outside Earth’s protective atmosphere.
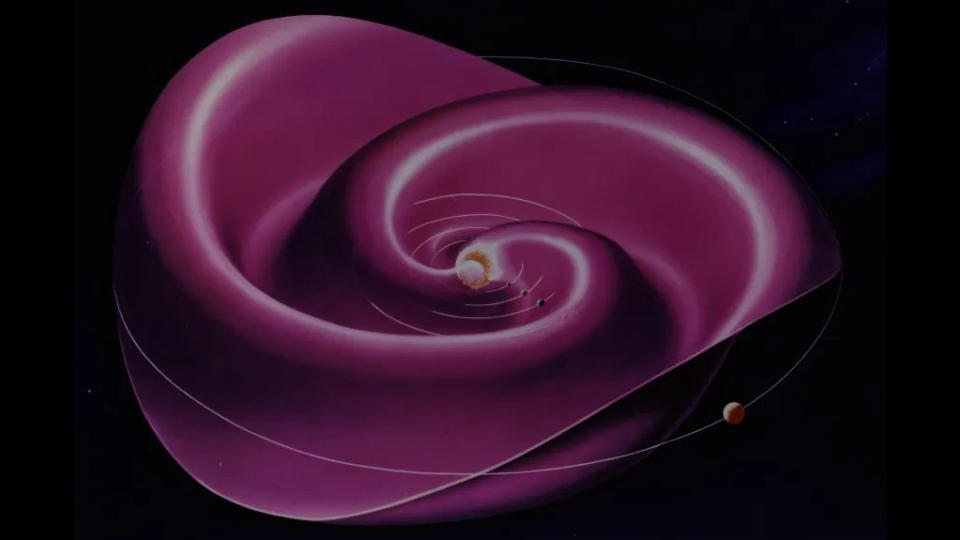
As the sun’s magnetic field shifts, the “current sheet” — a sprawling surface that radiates billions of miles out from the sun’s equator — becomes very wavyproviding a better barrier against cosmic rays.
Predict the strengths of the solar system in the future
Scientists will be watching the reversal of the sun’s magnetic field and seeing how long it takes for it to bounce back into a dipole configuration. If that happens within the next few years, the next 11 year cycle will be quite active, but if the build is slow, the cycle will be quite weak, like the previous 24 Solar Series.