When will we be able to see the planets at their best during the next year of 2024? Well, this guide will tell you. It will also provide information on when a particular planet may be passing by another planet, or a bright star for that matter, as well as the constellation each of them will occupy during the year. Read on to learn more about various factors such as conjunctions, oppositions and elongations that make up next year’s skywatching schedule.
1. Mercury
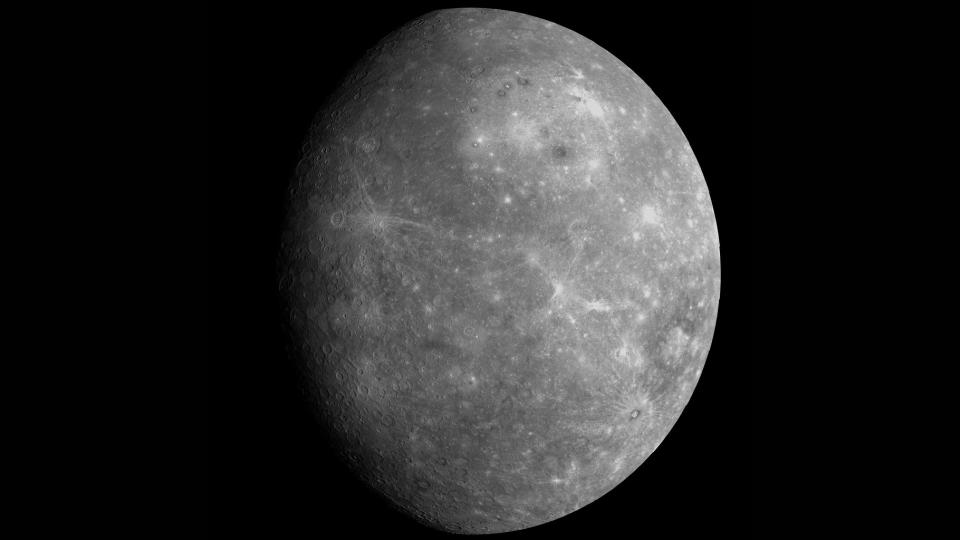
As an evening star, mercury appears in the western sky and sets about an hour later the sun does. As the morning star, it is visible in the eastern sky, rising about an hour before the sun. There must be a clear, unobstructed horizon on these occasions. Mercury is usually seen as a bright “star” with a yellow or ocher hue. You can view the planet in the morning from January 5th to January 26th, May 2nd to May 23rd, August 30th to September 19th and December 18th to December 31st. You can also take some measures of Mercury in the evenings of March 10 to March 31, July 8 to July 29 and November 2 to November 23.
There will be mercury brighter and easier to see in the evening sky between March 10 and March 31, and brighter and easier to see in the morning sky between 5 January to 26 January and again between 18 December and 31 December.
2. Venus
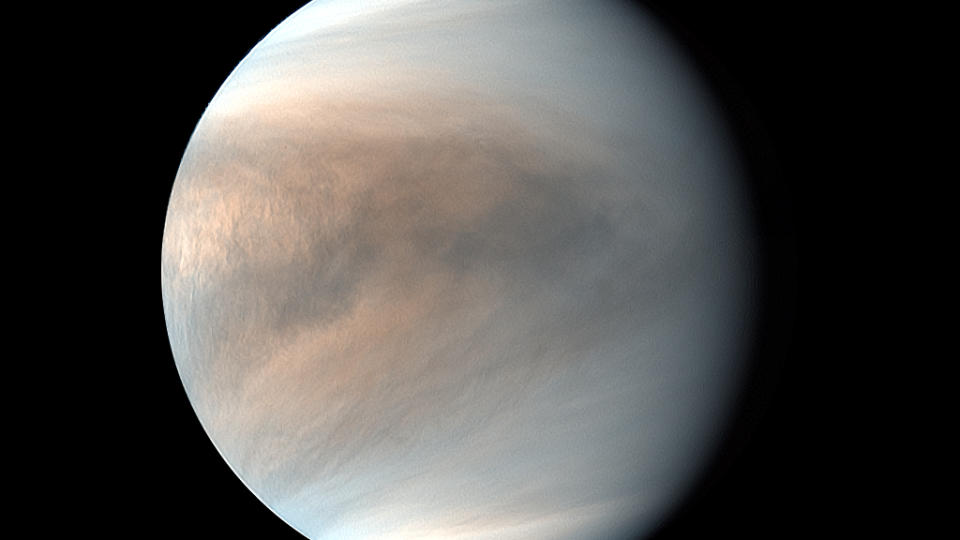

Always amazing, and shining with a steady, silvery light, you can catch Venus during the morning in the eastern sky at dawn from January 1 to April 8; evening in the western sky at dusk from 30 July to 31 December.
The IS The time to see Venus in the morning sky is in 2024 it will come from January 1 to February 11. The the best time to see Venus in the evening sky in 2024 from 5 October to 31 December. On February 22, Venus will be very close to you Mars (passing 0.6 degrees north of the Red Planet). Venus and Saturn seen very close together (Venus direct 0.2-degree N) on the morning of March 21.
On April 3, Venus will slip just 0.3 degrees S Neptune. On August 5, Venus will pass 1.1 degrees N of bluish Regulus, the brightest star in the constellation Leo, the Lion. On November 22, Venus passed 1.1 degrees north of Nunki, a second-magnitude star in the constellation Sagittarius.
3. Mars
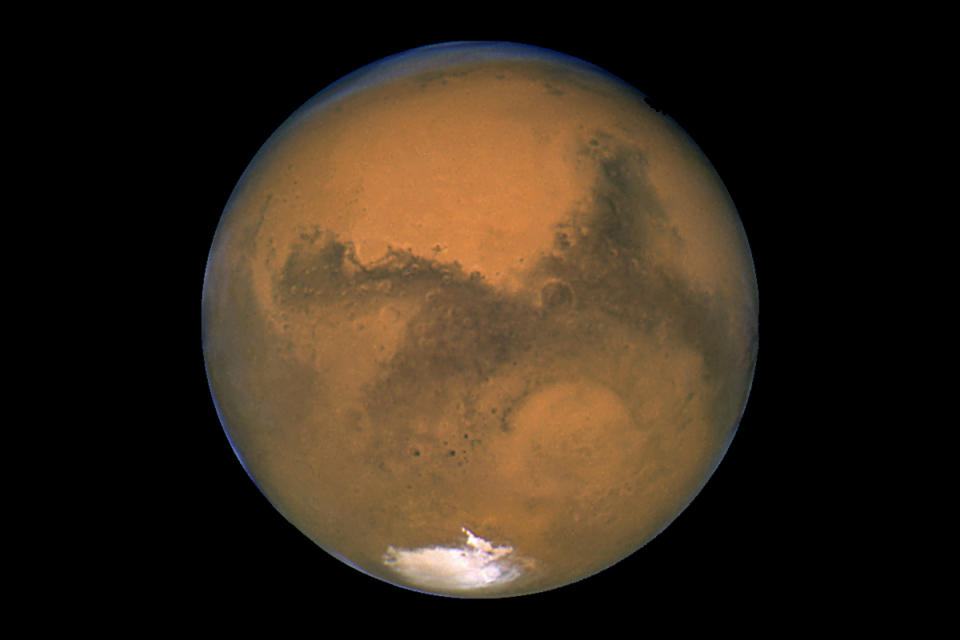


This will be another “off” year for Mars, as for much of 2024 it will appear relatively faint in the morning sky. Mars will be effectively invisible for the first 10 days of the new year, immersed too deep in the bright glow of the day to see. On New Year’s Day it will reside in the constellation of Sagittarius, a distance of 225.2 million miles (362.4 million kilometers) from World. By April Fool’s Day, it will be in the constellation of Aquarius and visible low in the southeast for a few hours before sunrise, shining at size +1.2. On July 1, it will be visible after midnight in the eastern sky, having brightened slightly to magnitude +1.0.
On Halloween, during the late hours of the night, Mars will be easily visible in the northeast sky, with the “Twin Stars” of Gemini, Castor and Polluxpointing directly at this yellow-orange planet, now shining at magnitude +0.1.
From then on, through the balance of the year, Mars will increase rapidly as it approaches Earth. It will stand out against the starry background of space on December 6, performing a retrograde loop as a prelude to its first opposition since 2022 on January 16, 2025. On New Year’s Eve, now in the constellation of Cancer, Mars will be 61.3 million miles (98.6 million km) from Earth and shine at magnitude -1.2 , which is only slightly dimmer than Siriusthe brightest star in the the night sky; this will be the brightest in 2024.
Mars will pass 2.7 degrees north of the second magnitude star Nunki in the constellation Sagittarius on January 21st and will come very close to Venus (passing 0.6 degrees south of that bright world) on February 22nd. 0.4-degree N) on April 10 and to Neptune (0.1-degree S) on April 29. The Red Planet will pass 4.9 degrees north of the same bright and orange-tinted star Aldebaran on August 4 and slip 0.3-degrees north of Jupiter on 14 August.
Finally, in the early morning of December 18, a faint gibbous moon will slide over Mars. Throughout the northern parts of North America, the moon There will be an actual occultation, or eclipse, of the planet.
4. Jupiter
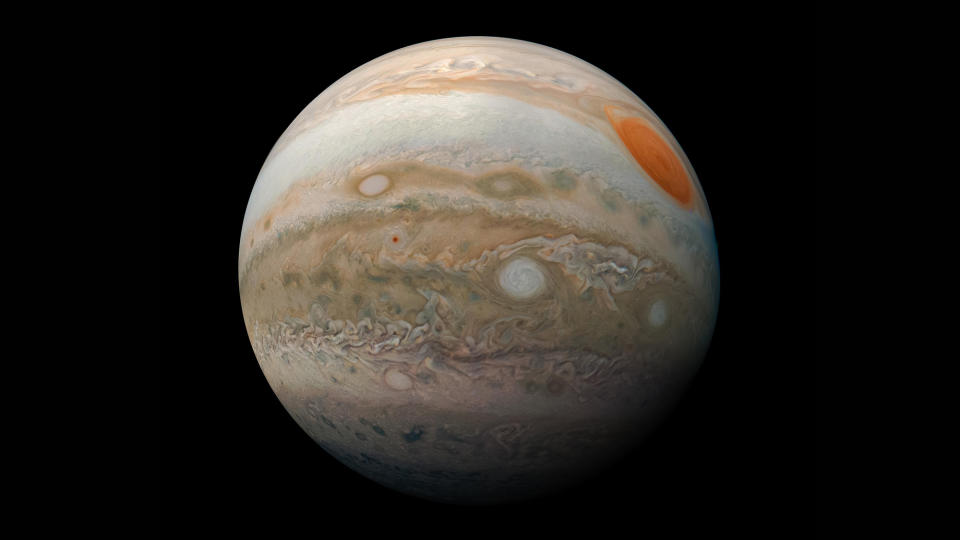


Jupiter will be stunning with a silver-white luster in 2024. It starts the year in the constellation Aries the Ram, then crosses into Bull the Taurus on April 28 where it will remain for the balance of the year.
During the nights from 1 January to 26 April, it will shine brightly, as well as during the mornings from 8 June to 6 December. Evening viewing will again be the best since December. 7 to 31 December.
He is will be brighter in 2024 14 November to 28 December. Jupiter will oppose the sun on December 7th. It will pass 4.8 degrees north of the first large star Aldebaran on July 9 and will be only 0.3 degrees south of distant dimensions. Mars on August 14.
5. Saturn
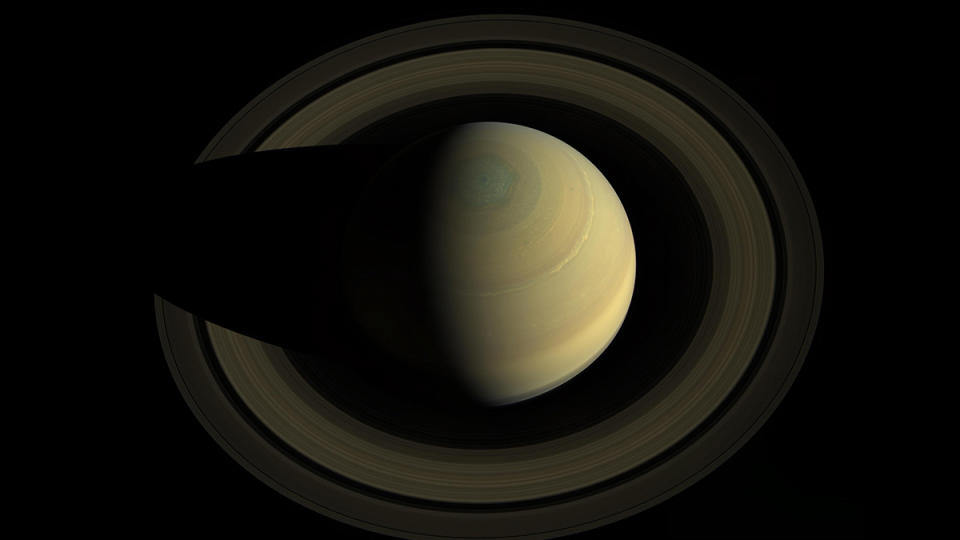

Saturn shines like a yellowish-white “star” of moderate brightness. The famous rings, however, are only visible in a telescope.
The rings were at their maximum inclination towards Earth in October 2017, but are now rapidly approaching our line of sight. They will reach the edge of the Earth in the spring of 2025. The process will begin in 2024 within the boundaries of the constellation of Aquarius, the Water Bearer, and the planet will remain there for the rest of the year.
You can catch Saturn in the evenings from January 1st to February 11th, mornings from March 17th to September 7th, then again in the evenings from September 8th to December 31st. Saturn’s brightest in 2024 fall between 25 August and 1 October. Saturn will be in opposition to the sun on September 8th. Saturn and Venus will appear close together (with Saturn only 0.2 degrees S) on the morning of March 21st and will be 0.4-degrees S of Mars on April 10th.
6. Uranus
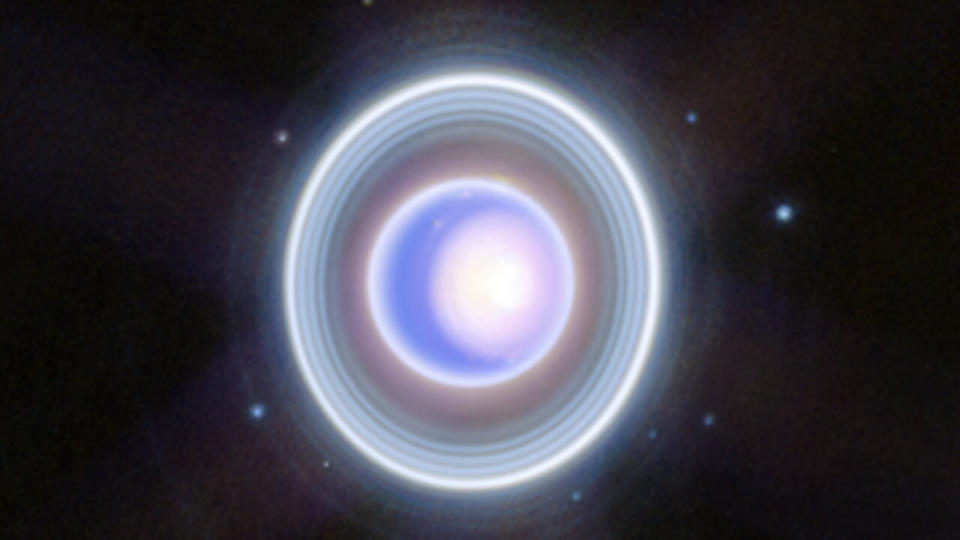


People blessed with good eyesight and a clear, dark sky can see Uranus with the naked eye, as well as first-hand knowledge of exactly where to look for it.
At its brightest, this planet shines at magnitude +5.6 and can be easily identified with good binoculars. A small telescope can reveal its tiny greenish disc. Uranus he spends the entire year 2024 in the constellation Aries the Ram. You can see it in the evenings from 1 January to 27 April, mornings from 31 May to 16 November, then again in the evenings from 17 November to 31 December. It is brightest in 2024 will take place from 15 October to 21 December. Uranus will oppose the sun on November 16th.
7. Neptune
Last but not least, Neptune will spend all of 2024 in the constellation of Fishes. At a peak magnitude of +7.8, this blue-green world is only visible with good binoculars or a telescope. It will be in the sky for optimal viewing during evenings from 1 January to 1 March, mornings from 3 April to 19 September, then again in the evenings from 20 September to 31 December.
It is brightest in 2024 will take place from 23 July to 19 November. The opposition is there on 20 September. Two great opportunities to spot Neptune will come first on April 3, when Venus slips 0.3-degree S of Neptune, and again on April 29, when Mars passes just 0.1-degree S of Neptune. Keep in mind that compared to Neptune, Mars will appear over 500 times brighter and Venus 58,000 times brighter.